PCB之HDI板 盲孔底部ICD问题 原因分析及改善
PCB HDI Board Blind Via Bottom ICD Issue: Cause Analysis and Improvement
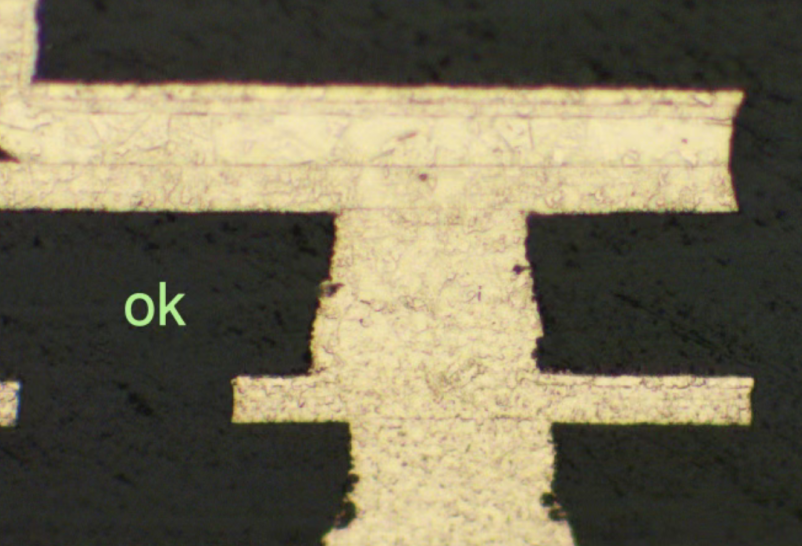


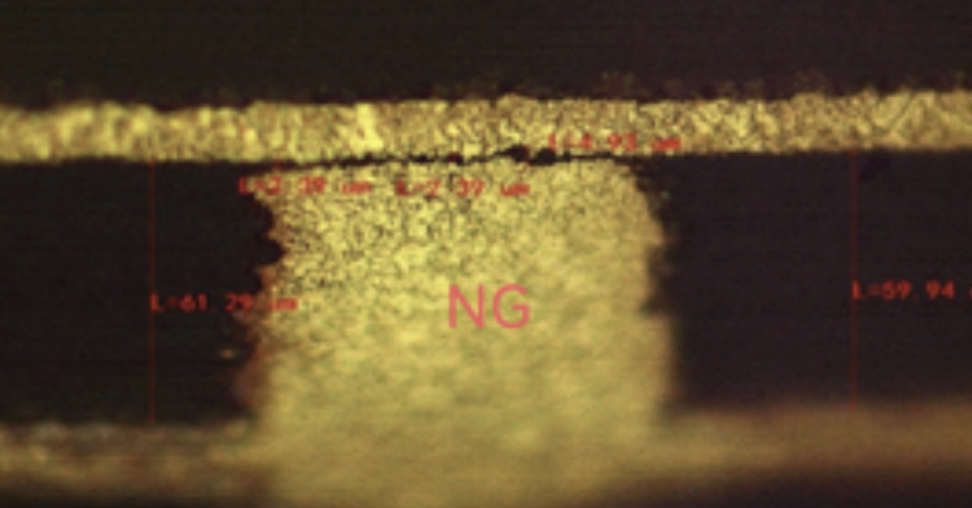
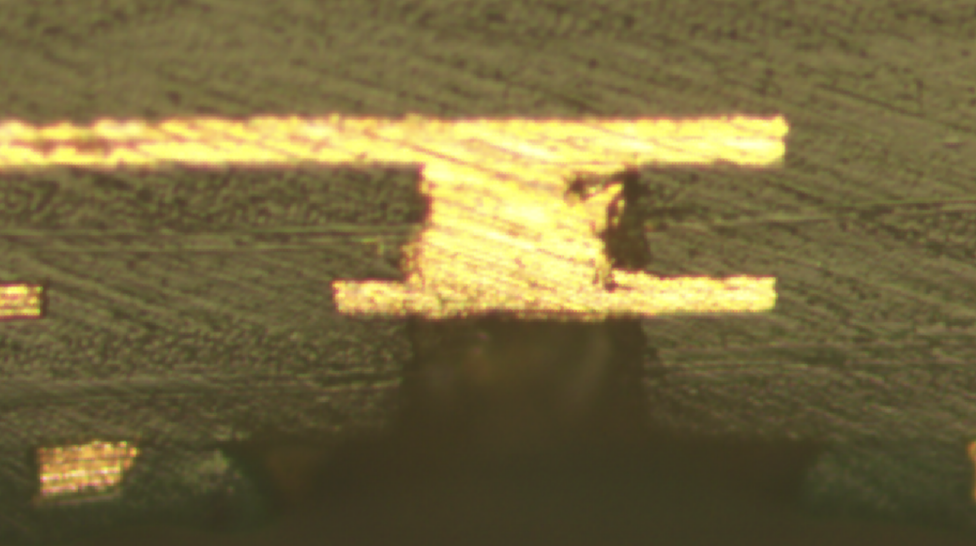
这些缺陷会直接导致孔金属化后电气连接不可靠,表现为高电阻、间歇性导通或完全开路,且在后续热应力(如回流焊)中故障会进一步加剧。
These defects directly lead to unreliable electrical connections after metallization, manifesting as high resistance, intermittent conduction, or complete open circuits. Additionally, failures may worsen under subsequent thermal stress (e.g., reflow soldering).
化学除胶和等离子除胶是彻底清除这些缺陷、获得一个洁净且活性化的铜表面的最关键工序。任何在此环节的失效都将直接导致ICD。
Chemical desmearing and plasma desmearing are the most critical processes for thoroughly removing these defects and obtaining a clean and activated copper surface. Any failure in these steps will directly result in ICD.
二、 根本原因分析
II.Root Cause Analysis
此问题的根源集中于激光钻孔和钻孔后处理工序。
The root cause of this issue lies primarily in the laser drilling and post-drilling treatment processes.
1. 激光钻孔参数不当
Improper Laser Drilling Parameters
能量过高/脉冲数过多: 过强的激光能量在烧穿介质层后,剩余能量继续作用在下方的铜面上。铜吸收热量后迅速升温、熔化甚至气化,导致铜面被损伤,出现凹坑、裂纹或晶格损伤。
Excessive Energy/Too Many Pulses: After penetrating the dielectric layer, excess laser energy continues to act on the underlying copper surface. The absorbed heat causes rapid temperature rise, melting, or even vaporization of the copper, resulting in pits, cracks, or lattice damage.
能量过低/脉冲数不足: 能量不足以完全烧蚀干净介质层,导致树脂残渣(Smear)或碳化物残留附着在孔底铜面上。这些残留物是绝缘的,会阻碍化学铜沉积,形成连接缺陷。
Insufficient Energy/Too Few Pulses: The energy is inadequate to completely ablate the dielectric layer, leading to resin residue (smear) or carbide deposits adhering to the copper surface at the bottom of the via. These residues are insulating and hinder chemical copper deposition, causing connection defects.
焦距不准: 激光焦点没有准确落在介质层与铜层的界面上,导致钻孔效率低下,能量分布不均,更容易造成残胶或铜损伤。
Incorrect Focal Length: The laser focus is not accurately set at the interface between the dielectric layer and the copper layer, resulting in inefficient drilling, uneven energy distribution, and a higher likelihood of resin residue or copper damage.
2. 化学除胶工艺失效
2. Failure of Chemical Desmearing Process
化学除胶(高锰酸盐体系)是传统且主流的工艺,其失效模式复杂:
Chemical desmearing (using a permanganate-based system) is a traditional and mainstream process, with complex failure modes:
药水活性不足:
Inadequate Chemical Activity:
高锰酸钾浓度衰减: KMnO₄在反应中不断被消耗还原为MnO₂,若浓度不足,氧化能力下降,无法有效断裂树脂长分子链。
Depleted KMnO₄ Concentration: KMnO₄ is continuously consumed and reduced to MnO₂ during the reaction. If the concentration is insufficient, its oxidizing capacity decreases, rendering it ineffective in breaking the long molecular chains of the resin.
· NaOH浓度失衡: 碱浓度过低,无法提供足够的OH⁻来维持反应速率和溶解氧化产物;碱浓度过高,可能对玻璃布产生过度侵蚀。
Imbalanced NaOH Concentration: Low alkali concentration fails to provide enough OH⁻ to sustain the reaction rate and dissolve oxidation products; excessive alkali concentration may over-etch the glass cloth.
药水寿命过长: 药液中溶解的铜离子(Cu²⁺)浓度累积,会催化分解高锰酸钾,大幅降低其有效寿命和氧化能力。
Extended Chemical Lifespan: Accumulated copper ions (Cu²⁺) in the solution catalyze the decomposition of KMnO₄, significantly reducing its effective lifespan and oxidizing capacity.
温度偏低: 氧化反应速率随温度指数级增长。温度不达标是除胶不净的最常见原因之一。
Low Temperature: The oxidation reaction rate increases exponentially with temperature. Suboptimal temperature is one of the most common causes of incomplete desmearing.
时间不足: 包括溶胀、氧化、中和各槽的时间不足,特别是氧化时间,无法保证药水充分进入并完全处理微盲孔底部。
Insufficient Time: Inadequate time for swelling, oxidation, and neutralization steps, particularly oxidation time, prevents the chemicals from fully penetrating and treating the bottom of the micro blind vias.
· “再污染”问题: 中和(还原)阶段使用的酸肼(或硫酸羟胺)等还原剂若浓度或时间不足,无法彻底清除孔壁吸附的MnO₂胶体颗粒,这些MnO₂残留物本身就是绝缘的ICD。
"Recontamination" Issue: If the concentration or time of reductants like acid hydrazine (or hydroxylamine sulfate) used in the neutralization (reduction) stage is insufficient, MnO₂ colloidal particles adsorbed on the via walls cannot be completely removed. These MnO₂ residues are inherently insulating and contribute to ICD.
3. 等离子除胶工艺的局限性
3. Limitations of Plasma Desmearing Process
等离子体处理作为物理化学方法,也有其特定的失效点:
Plasma treatment, as a physico-chemical method, also has specific failure points:
气体配方选择错误:
Incorrect Gas Formulation:
仅使用O₂:主要用于去除有机污物(残胶),但对顽固碳化物的去除能力有限。
Using Only O₂: Primarily effective for removing organic contaminants (resin residue) but has limited capability against stubborn carbides.
忽略CF₄/NF₃等含氟气体:对于激光产生的极度惰性的碳化物,必须引入含氟气体生成挥发性的CF₄等物质才能有效去除。这是等离子处理能否彻底清除ICD的关键。
Neglecting CF₄/NF₃ and Other Fluorinated Gases: To remove highly inert carbides generated by laser drilling, fluorinated gases must be introduced to form volatile compounds like CF₄. This is critical for the plasma process to effectively eliminate ICD.
· 穿透性与均匀性问题:
Penetration and Uniformity Issues:
对于深宽比大的盲孔,等离子体的活性基团可能无法充分到达孔底,导致孔口清洁而孔底残留(微观上的“孔口效应”)。
For blind vias with high aspect ratios, active plasma species may not adequately reach the bottom, resulting in clean via openings but residual contaminants at the bottom (microscopic "aperture effect").
设备腔体内的真空度、功率、气体流量等参数设置不佳,会导致处理不均匀,批次稳定性差。
Poor parameter settings such as vacuum level, power, and gas flow rate in the equipment chamber can lead to uneven treatment and poor batch consistency.
前道污染: 如果激光钻孔后板面有油污或其他污染物,会阻挡等离子体与残胶的有效接触。
Contamination from Previous Steps: If oil stains or other contaminants are present on the board surface after laser drilling, they can block effective contact between the plasma and the resin residue.
4. 两种工艺的协同失效
4. Synergistic Failure of Both Processes
· 工艺选择错误: 对于具有高厚径比或使用高性能材料(如Low-loss PP) 的盲孔,高频高速材料及PTFE材料、 PI、聚酰亚胺、BT、陶瓷材料、碳氢化合物等特殊材料,化学除胶的药水交换能力可能不足,或者仅靠化学除胶,无法攻击到特殊材料的“要害部位”, 此时必须采用等离子处理作为主导或辅助。
Incorrect Process Selection: For blind vias with high aspect ratios or those using high-performance materials (e.g., Low-loss PP, high-frequency materials, PTFE, PI, polyimide, BT, ceramic materials, hydrocarbons), the exchange capacity of chemical desmearing may be insufficient, or chemical desmearing alone may not address the critical areas of special materials. In such cases, plasma treatment must be employed as the primary or auxiliary process.
顺序与搭配不当: 对于严重碳化的ICD,最有效的流程是 “等离子先行破除碳化层 + 化学跟进清除氧化残留” 的组合拳。顺序颠倒或省略步骤都会导致处理不彻底。
Improper Sequence and Combination: For severely carbonized ICD, the most effective Flow is a combination of "plasma treatment first to break down the carbonized layer + chemical treatment follow-up to remove oxidation residues." Reversing the sequence or omitting steps will result in incomplete treatment.
三、 专业级改善措施
III. Professional-Grade Improvement Measures
改善核心在于优化激光钻孔工艺和确保除渣效果。
The core of improvement lies in optimizing the laser drilling process and ensuring effective desmearing.
1. 优化激光钻孔工艺(从源头杜绝)
1. Optimize Laser Drilling Process (Prevent at the Source)
进行激光参数 DOE 实验: 针对特定的介质材料厚度和类型,系统性地测试并找到最佳的激光能量、脉冲次数、焦距和重复频率的组合。
Conduct DOE for Laser Parameters: Systematically test and identify the optimal combination of laser energy, pulse count, focal length, and repetition rate for specific dielectric material thicknesses and types.
目标: 达到“刚好清除干净介质层,并完整露出光滑、无损伤的内层铜面”的临界状态。
Goal: Achieve the critical state of "just completely removing the dielectric layer and exposing a smooth, undamaged inner copper surface."
方法: 通过制作大量切片,在金相显微镜下观察孔底形貌,以确定最佳参数窗口。
Method: Determine the optimal parameter window by examining via bottom morphology under a metallurgical microscope through extensive cross-sectioning.
采用波长更合适的激光器: CO2激光(波长9.4μm)容易被树脂吸收,而UV紫外激光(波长355nm)更容易被铜吸收。因此,通常用CO2激光烧蚀介质层,用UV激光精细加工或清洗。确保工艺匹配。
Use Lasers with More Suitable Wavelengths: CO₂ lasers (wavelength 9.4μm) are readily absorbed by resin, while UV lasers (wavelength 355nm) are more easily absorbed by copper. Thus, CO₂ lasers are typically used to ablate the dielectric layer, and UV lasers are used for fine processing or cleaning. Ensure process matching.
2. 实施实时监控: 使用配备电光学监测系统的先进激光钻机,其能通过监测激光打孔时产生的等离子体闪光信号来判断是否刚好打穿介质层(信号会发生突变),从而实现自动终止钻孔,防止过钻损伤铜层。
2. Implement Real-Time Monitoring: Use advanced laser drilling machines equipped with electro-optical monitoring systems that detect plasma flash signals generated during drilling to determine whether the dielectric layer has just been penetrated (signal突变) and automatically terminate drilling to prevent over-drilling and copper damage.
3. 强化除渣/清洁工艺优化除渣参数: 增加高锰酸钾浓度、升高处理温度或延长处理时间,以确保能彻底清除孔底的树脂残渣和碳化物。但需注意避免“过除渣”导致玻璃纤维突出。
Strengthen Desmearing/Cleaning Process, Optimize Desmearing Parameters: Increase KMnO₄ concentration, raise processing temperature, or extend processing time to ensure complete removal of resin residue and carbides at the via bottom. However, avoid "over-desmearing," which may cause glass fiber protrusion.
考虑增加等离子体处理: 对于高端产品,在化学除渣前增加等离子清洗,能非常有效且均匀地去除微小的残胶和碳化物,尤其对深窄盲孔效果显著。
Consider Adding Plasma Treatment: For high-end products, adding plasma cleaning before chemical desmearing can very effectively and uniformly remove微小残胶 and carbides, particularly for deep and narrow blind vias.
2.1. 化学除胶工艺优化
2.1Optimize Chemical Desmearing Process
· 实施严格的药水管控:
· Implement Strict Chemical Control:
· 建立自动滴定分析系统,实时监控KMnO₄和NaOH的浓度,并设定严格的补加和报废标准。
Establish an automatic titration analysis system to monitor KMnO₄ and NaOH concentrations in real time, with strict replenishment and discard criteria.
· 监控药水中Cu²⁺离子浓度,当其达到临界值(如>35ppm)时,果断报废整缸药水。
Monitor Cu²⁺ ion concentration in the chemical solution and discard the entire tank when it reaches a critical value (e.g., >35ppm).
· 参数DOE与权威认证:
Parameter DOE and Authoritative Certification:
· 通过实验设计(DOE)找到溶胀、氧化、中和三步骤的最佳温度、时间组合。必须通过切片+SEM扫描电镜来验证孔底效果,而非仅凭表面现象判断。
Use Design of Experiments (DOE) to find the optimal temperature and time combination for the swelling, oxidation, and neutralization steps. Effectiveness must be verified via cross-sectioning and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope) examination of the via bottom, not just surface phenomena.
· 对除胶后品质进行定量评估,如采用染色测试或热应力测试后切片观察,确保连接的可靠性。
Conduct quantitative evaluation of post-desmearing quality, such as dye penetration tests or thermal stress tests followed by cross-sectioning, to ensure connection reliability.
· 升级药水体系: 对于高端产品,考虑采用更先进的化学体系,如部分公司采用的有机酸体系除胶剂,其对不同材料兼容性更好,副作用更小。
Upgrade Chemical Systems: For high-end products, consider adopting more advanced chemical systems, such as organic acid-based desmear agents, which offer better compatibility with different materials and fewer side effects.
2.2 等离子除胶工艺升级
2.2 Upgrade Plasma Desmearing Process
· 采用“混合气体配方”策略:
· 标准配方: O₂ + CF₄ / NF₃。CF₄在等离子环境中产生的氟自由基能高效蚀刻碳硅键,彻底清除碳化物。
· 添加惰性气体: 加入Ar、He等气体可以提高等离子体密度和稳定性,增强处理均匀性。
Adopt "Mixed Gas Formulation" Strategy:
Standard Formulation: O₂ + CF₄ / NF₃. Fluorine radicals generated from CF₄ in the plasma environment efficiently etch carbon-silicon bonds, thoroughly removing carbides.
Add Inert Gases: Incorporating gases like Ar or He can increase plasma density and stability, enhancing treatment uniformity.
· 优化设备参数与维护:
· 与设备厂商合作,通过实验找到针对不同介质材料的最佳功率、真空度、气体比例和处理时间。
· 定期进行设备保养,清洁腔体、校准气体流量计,确保工艺的重复性。
Optimize Equipment Parameters and Maintenance:
Collaborate with equipment suppliers to experimentally determine the optimal power, vacuum level, gas ratio, and processing time for different dielectric materials.
Perform regular equipment maintenance, clean the chamber, and calibrate gas flow meters to ensure process repeatability.
· 作为必选工艺: 对于任何≥3阶的HDI板、任何使用ABF材料的载板,以及所有出现ICD问题的批次,应将等离子处理列为标准必选工艺,而非可选或补救措施。
Make It a Mandatory Process: For any HDI boards with ≥3 layers, any substrates using ABF materials, and all batches experiencing ICD issues, plasma treatment should be designated as a standard mandatory process, not an optional or remedial step.
3. 建立“化学+等离子”复合工艺流
3. Establish a "Chemical + Plasma" Composite Process Flow
· 推荐流程: 激光钻孔 → 等离子处理(主攻碳化物) → 化学除胶(清除氧化残留和中和) → 沉铜电镀。
优势: 等离子先破除最顽固的碳化层,为后续化学药水的渗透和反应打开通道,二者协同,可达到1+1>2的彻底清洁效果。
流程监控: 在等离子和化学除胶后,均可设置切片抽检点,监控各环节的输出质量,便于问题追溯。
Recommended Flow: Laser Drilling → Plasma Treatment (targeting carbides) → Chemical Desmearing (removing oxidation residues and neutralization) → Copper Deposition and Plating.
Advantage: Plasma first breaks down the most stubborn carbonized layer, creating channels for subsequent chemical penetration and reaction. The synergy between the two achieves a 1+1>2 effect for thorough cleaning.
Process Monitoring: Set up sampling points for cross-sectioning after plasma and chemical desmearing to monitor the output quality of each step, facilitating problem tracing.
4. 终极分析手段
4. Ultimate Analysis Methods
· 表面分析: 当出现ICD时,使用扫描电子显微镜(SEM) 观察形貌,并配合能量色散X射线光谱(EDS) 进行元素分析,是判断残留物成分(是C、O、还是F、Mn)的黄金标准,能直接锁定问题根源是在化学环节(Mn残留)还是等离子环节(C残留)。
Surface Analysis: When ICD occurs, use SEM to observe morphology and EDS (Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy) for elemental analysis. This is the gold standard for determining residue composition (whether it is C, O, F, or Mn), directly identifying whether the root cause lies in the chemical process (Mn residue) or plasma process (C residue).
5. 加强检测与监控
5. Enhance Detection and Monitoring
· 切片分析常态化: 定期取样进行金相切片分析,在200倍及以上的显微镜下重点检查盲孔底部的铜面状况,这是发现ICD最直接的手段。
· 采用扫描电子显微镜: 对于疑难问题,可使用SEM观察孔底的微观形貌,能更清晰地看到裂纹和残胶。
· 表面分析仪器: 可使用X射线光电子能谱仪等设备分析孔底残留物的化学成分,判断是树脂还是碳化物,从而溯源问题根源。
Regular Cross-Section Analysis: Periodically sample and perform metallographic cross-section analysis, focusing on the copper surface condition at the blind via bottom under a microscope at 200x magnification or higher. This is the most direct method for detecting ICD.
Use Scanning Electron Microscope: For疑难问题, use SEM to observe the microscopic morphology of the via bottom, providing clearer visibility of cracks and resin residue.
Surface Analysis Instruments: Use equipment like X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) to analyze the chemical composition of residues at the via bottom, determining whether it is resin or carbide to trace the problem source.
总结
盲孔底部ICD问题的解决,绝非泛泛而谈的参数调整,其核心在于:核心改善思路是:
Summary
Resolving the ICD issue at the bottom of blind vias is not about vague parameter adjustments. The core improvement strategies are:
1. 精调激光参数,找到“刚好打穿”的甜蜜点。
Precisely adjust laser parameters to find the "sweet spot" of just penetrating.
2. 强化除渣工艺,确保孔底绝对清洁。
Strengthen the desmearing process to ensure absolute cleanliness at the via bottom.
3. 通过高频次的切片监测,持续监控工艺稳定性。
Continuously monitor process stability through high-frequency cross-section inspections
4. 精准识别ICD类型:是残胶?碳化物?还是MnO₂残留?
Accurately identify the type of ICD: Is it resin residue, carbide, or MnO₂ residue?
5. 深度优化核心工艺:化学除胶的关键是“药水活性管控”;等离子除胶的关键是“含氟气体配方”。
Deeply optimize core processes: The key to chemical desmearing is "chemical activity control"; the key to plasma desmearing is "fluorinated gas formulation."
6. 建立复合工艺流:对于高端产品,“等离子+化学”的组合是解决顽固ICD的最有效方案。
Establish a composite process flow: For high-end products, the combination of "plasma + chemical" is the most effective solution for stubborn ICD.
7. 依托尖端检测设备:依赖SEM/EDS等工具进行根源分析,而非仅凭经验猜测。
Rely on advanced detection equipment: Use tools like SEM/EDS for root cause analysis, rather than relying solely on empirical guesses.
特别说明:以上的探讨仅供参考,起到抛砖引玉的作用!
Special Note: The above discussion is for reference only, aiming to stimulate further exploration!
来源:整理自互联网资料,供大家交流学习之用。
Source: Compiled from online materials for communication purposes.

No.206, Yongning Industry Zone, Fenghuangbei Road, Zengcheng District, Guangzhou, China

